
Enhancing Accuracy in Remote Identity Verification: Beyond Reading ID Cards
(This is a part of the series about remote identity verification solutions and how to successfully integrate them ...
Read more

This is a part of the series about remote identity verification solutions and how to successfully integrate them into your business. For all parts of the series, click here.
What you’ll learn in this part:
The onboarding process is the gateway to any successful customer relationship, especially when it comes to digital identity verification. Organizations must be flexible to control and customize how they onboard their customers to maintain security and accuracy.
Onboarding is the first step in establishing a relationship with new customers. It involves collecting personal information, verifying identity, and ensuring that the person entering your system is who they claim to be. For businesses, having control over this process is critical because it directly impacts security, customer experience, and compliance with legal regulations.
Businesses in different sectors have unique onboarding needs. A bank may require additional checks compared to an e-commerce platform. By customizing the onboarding process, businesses can create tailored customer journeys that align with their operational and regulatory requirements.
Regulations such as Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) often vary by country or region. A customizable onboarding solution enables businesses to adjust their processes to comply with these legal frameworks without compromising efficiency.


Moreover, having control over the onboarding flow ensures a balance between user experience and security. By integrating tools that allow for customization, businesses can automate certain parts of the process while adding additional layers of verification where necessary.
Digital Identity Service (DIS) is a suite of technologies designed to manage and verify digital identities remotely. It plays a crucial role in the onboarding process by ensuring that the individual or entity attempting to access a service is legitimate. With the rise of remote services, having a robust DIS is no longer optional but a requirement for any business operating in banking, telecommunications, or e-commerce.
Digital Identity Service solutions consist of two main components: Customer Onboarding and Face Biometrics. Each of these plays a vital role in securing the onboarding process.
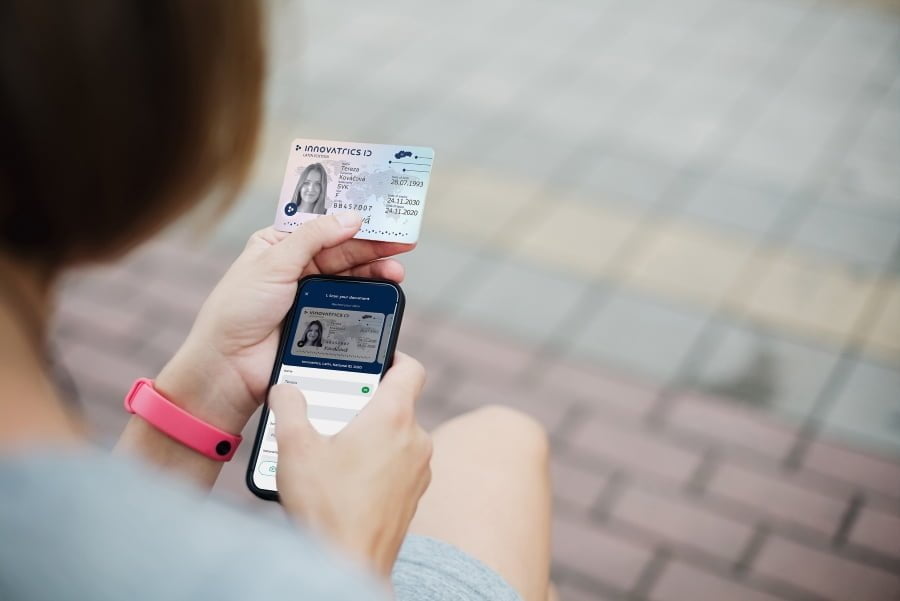
Customer onboarding through DIS is designed to gather, process, and seamlessly verify identity information. Automated document capture, OCR technology, and AI-driven analytics allow businesses to reduce manual intervention by quickly extracting information from ID cards, passports, and other documents while maintaining high levels of accuracy.
Nowadays, artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms streamline the onboarding process, reducing errors and ensuring that identity information is validated in real time.
Face biometrics is the other key feature of modern DIS solutions. It involves verifying the identity of a user by analyzing their facial features and comparing them with the information provided in their identity documents. Face biometrics ensures that the person in front of the camera matches the photo on their ID. This prevents identity fraud by ensuring that a live person is present during the verification process.
Face biometrics solutions now integrate liveness detection to ensure that users are not using photos, videos, or masks to impersonate others, strengthening the overall security of the onboarding process.
One of the often-overlooked aspects of onboarding is identity deduplication. In large databases, duplicate records can lead to inefficiencies, security vulnerabilities, and compliance risks. Deduplication ensures that each user or entity in the system has only one unique identity, reducing the potential for fraud and improving data quality.
Bad actors can exploit duplicate identities in a system for fraudulent purposes. For example, a person might create multiple accounts using different versions of their identity information to bypass limits or gain access to restricted services. This is unfortunately more prevalent in countries without proper or secure ID systems. Identity deduplication helps prevent this by ensuring that only one record exists per individual.
Inconsistent or duplicated data can cause confusion and errors in a business’s operations. Deduplication ensures that identity data is accurate, up-to-date and complete, which improves overall data integrity.
Identity deduplication is especially important in industries such as banking, where a single customer might attempt to create multiple accounts. By implementing deduplication at the onboarding stage, businesses can ensure that their databases remain clean and secure.
When designing a digital onboarding flow, setting up thresholds for verification is critical to balancing security and user experience. Thresholds define the acceptable levels of certainty needed to approve or flag an onboarding attempt, based on criteria such as biometric matches, document authenticity, and identity checks.
By setting up appropriate thresholds, businesses can fine-tune their onboarding processes to reduce friction for legitimate users while catching fraudulent attempts. Lower thresholds may increase the risk of fraud, while higher thresholds may result in too many false rejections. Finding the right balance is key to ensuring a smooth onboarding experience without compromising security.
Moreover, thresholds allow businesses to automate decision-making during the onboarding process. Based on preset confidence levels, the system can automatically approve, flag, or reject onboarding attempts. This reduces the need for manual review, speeding up the process while maintaining accuracy.
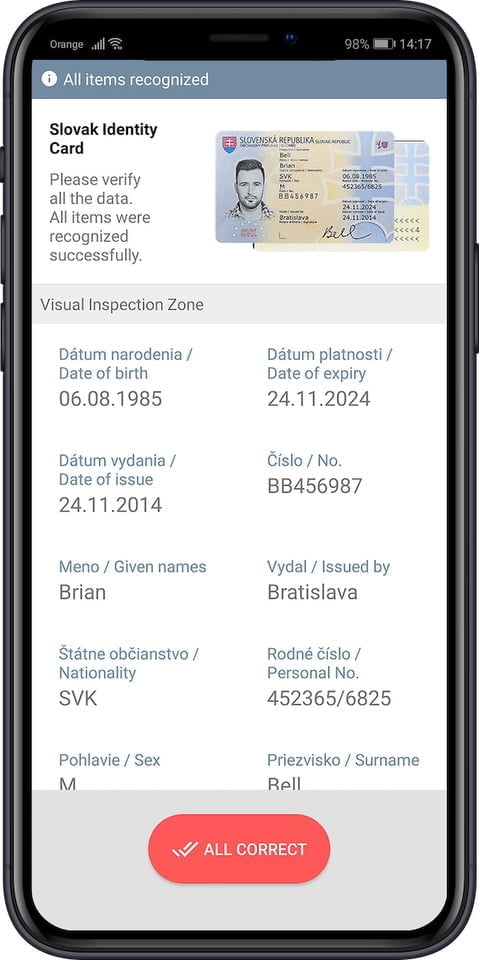

Setting appropriate thresholds allows businesses to adjust their onboarding process to different levels of risk. For instance, a high-risk banking transaction may require stricter thresholds compared to a low-risk e-commerce sign-up.
Facial Match Threshold: This determines how closely a user’s face must match the photo on their ID. If the match score falls below a certain threshold, the system may require additional verification steps.
Document Authenticity Threshold: This specifies the level of certainty required to verify that a scanned document is genuine. This can include checks for holograms, watermarks, or other security features.
Liveness Detection Threshold: This sets the confidence level for detecting whether a person is live during face biometric verification. Lower thresholds may allow for spoofing attacks, while higher thresholds may reject legitimate users in less-than-ideal conditions (e.g., poor lighting).
As digital identity verification continues to evolve, businesses must ensure that their onboarding flows are not only accurate but also adaptable to different scenarios. By controlling the onboarding flow with tools like Digital Identity Services, face biometrics, identity deduplication, and customizable thresholds, businesses can optimize their customer onboarding processes for both security and efficiency.
In today’s fast-paced digital world, having autonomy over the onboarding process is not just a benefit—it’s a necessity. By leveraging advanced technologies and carefully setting thresholds, businesses can ensure a seamless onboarding experience while maintaining the highest levels of security.
Looking for all or some of these technologies ready for easy integration?
You can find other parts of the Elements of Digital Onboarding Series here