OCR (Optical Character Recognition) definition
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is a technology that allows the digitization and conversion of printed or handwritten text into machine-readable format. OCR facilitates the ability to store, edit and search text electronically, potentially enhancing efficiency and productivity.
What is OCR (Optical Character Recognition)?
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is a technology that converts printed or handwritten text into a machine-readable format. By utilizing complex algorithms, OCR enables the digitization of documents, facilitating easier storage, editing, and searching of text electronically.
The applications of optical character recognition (OCR) range from archival preservation to streamlining administrative tasks in businesses, making it a valuable tool in various industries. With OCR, the time-consuming process of manual data entry and deciphering handwritten documents becomes a thing of the past, enhancing efficiency and productivity for individuals and organizations alike.
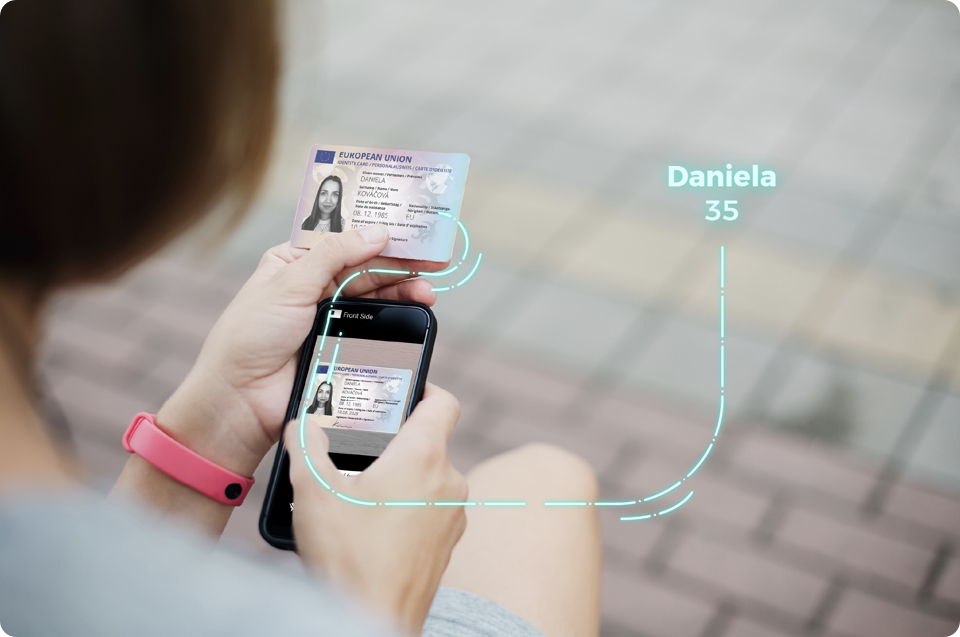

How Does Optical Character Recognition Technology Work?
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) works by leveraging advanced algorithms to analyze and interpret images or scanned documents containing printed or handwritten text. The process involves several key steps.
First, OCR software analyzes the input document, identifying different text areas and isolating individual characters or words. It then examines the shape, size, and stroke patterns of these elements to recognize and classify them.
Next, the software maps the recognized elements to a database of known characters, comparing the patterns to find the closest matches. Through machine learning and pattern recognition techniques, OCR software continuously improves its accuracy over time.
Once the characters are identified, OCR converts them into machine-readable formats such as ASCII or Unicode, enabling electronic storage, editing, and searching of the text. This transformation makes it possible to automate tasks like data entry, content extraction, and document indexing, offering substantial time and cost savings.
Overall, OCR technology plays a vital role in digitizing and transforming printed or handwritten text into accessible and editable digital content, introducing efficiency and convenience across various industries and applications.
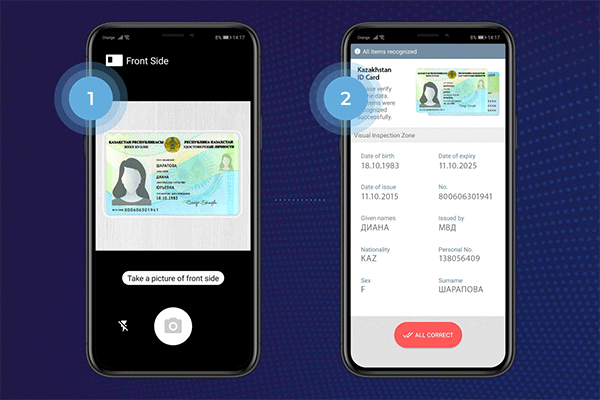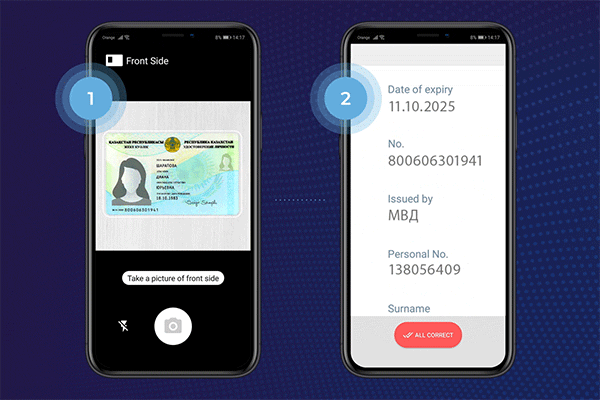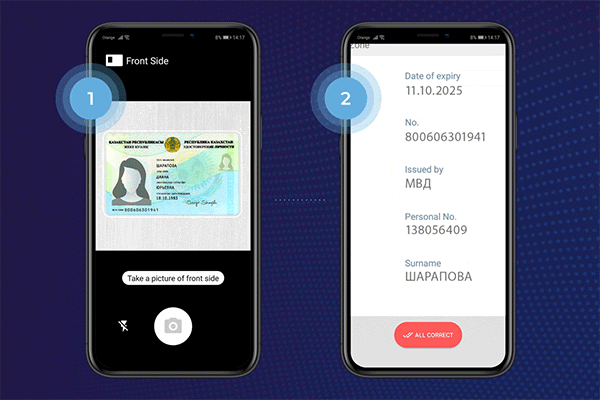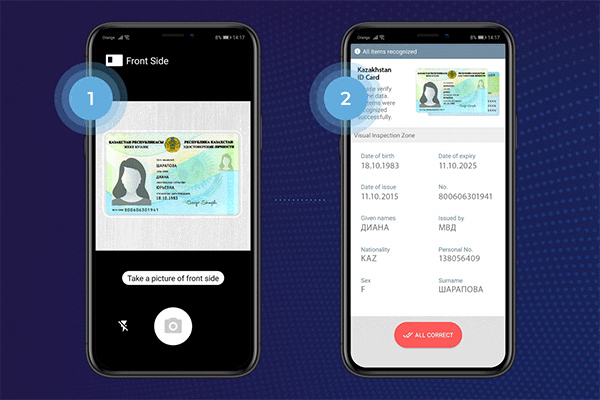
What is Optical Character Recognition Technology Used For?
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) has found numerous real-world applications across various industries. Here are some specific examples:
Identity Verification
OCR is used to extract information from identity documents such as passports, driver’s licenses, and ID cards. It can automatically recognize and extract relevant data like name, date of birth, address, and document numbers from these documents. This enables businesses to verify the identity of customers quickly and accurately during the onboarding process.
Passport and ID Card Verification
OCR technology aids in the automated verification of passports, driver’s licenses, and other identification documents. It enables the extraction of relevant information, such as name, date of birth, and document numbers, for authentication and validation purposes, enhancing security measures.
Healthcare Records
OCR plays a crucial role in digitizing patient records and medical documents in healthcare organizations. By converting handwritten or printed notes into electronic formats, OCR improves the accessibility, interoperability, and searchability of medical records, thus facilitating efficient healthcare services.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
OCR technology can help businesses comply with various regulatory requirements. It can extract specific data fields required for compliance, such as tax identification numbers or government-issued licenses, from documents. By automating the extraction of this information, OCR ensures that the onboarding process meets legal and regulatory obligations.
Automated Data Capture
OCR plays a crucial role in automating data capture from printed forms, surveys, and questionnaires. By extracting information from these documents, OCR facilitates the automatic input of data into databases or other software systems, eliminating the need for manual data entry.
Document Verification and Archiving
OCR is used to verify the authenticity of submitted documents and compare them with reference templates or databases. It can also convert physical documents into searchable and indexed digital formats, making it easier to archive and retrieve customer information for future reference.
Difference Between Optical Character Recognition and Optical Mark Recognition
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and Optical Mark Recognition (OMR) are both technologies used in document processing, but they serve different purposes.
OCR is primarily focused on converting printed or handwritten text into machine-readable and editable formats. It uses sophisticated algorithms to recognize characters, extract text, and recreate the document’s structure.
On the other hand, OMR is designed specifically to recognize and interpret marked areas or checkboxes on forms or surveys. OMR technology detects the presence or absence of marks or specific patterns and interprets them as data.
How Accurate is Optical Character Recognition?
The accuracy of Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology can vary depending on factors such as the quality of the input document and the complexity of the text. While there can be no single value that represents the accuracy of OCR across all scenarios, it is noteworthy that modern OCR systems can achieve high levels of accuracy.
Exploring the Benefits and Safety of OCR
Optical Character Recognition technology, when implemented and used securely, can offer several benefits in terms of safety and data protection. Here’s an explanation of OCR’s safety and its real-world benefits:
Data Security
OCR reduces the need for manual data entry, minimizing the handling of sensitive information by human operators. This reduces the risk of human error and unauthorized access, and thus enhances data security.
Data Access Control
OCR systems can implement access controls and user authentication mechanisms to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information. Role-based access controls and user permissions can be enforced to restrict access to confidential data, enhancing security and preventing unauthorized use or disclosure.
Compliance with Regulations
OCR helps businesses comply with data protection laws like GDPR in the EU. It ensures secure data handling, reducing the risk of non-compliance and legal issues.
Secure Collaboration and Sharing
OCR allows for secure collaboration and sharing of digitized documents. Instead of physically sharing paper-based documents, OCR enables secure digital sharing, reducing the risk of documents being misplaced, lost, or accessed by unauthorized individuals.

What are Examples of Optical Character Recognition Devices and Software?
Below are some of the most popular examples of optical character recognition (OCR) devices and software:
ABBYY Finereader
ABBYY FineReader is a popular OCR software that allows for accurate text recognition and conversion of scanned documents, PDFs, and images into editable and searchable formats.
Google Cloud Vision OCR
Google Cloud Vision OCR is a cloud-based OCR service offered by Google. It enables scanning and storing documents using OCR capabilities on smartphones and other devices.
Adobe Acrobat Pro
Adobe Acrobat Pro is a software suite that includes OCR functionality. It allows users to scan and convert paper documents into editable and searchable PDF files using OCR technology.
Textract by Amazon Web Services
Textract is a fully managed OCR service provided by Amazon Web Services. It is capable of accurately extracting text and data from various document formats, such as scanned images and PDFs.
How Does OCR Technology Recognize Characters in All Languages?
OCR technology can support and process most languages including Arabic, Hindi, Bengali, Chinese, Latin, Hebrew, and Urdu languages through the use of language-specific OCR models and recognition algorithms. OCR systems are designed to recognize characters and text patterns in images or documents and convert them into editable and searchable text.
For example, Innovatrics Digital Onboarding Toolkit (DOT) supports multiple languages, including Latin, Cyrillic, Arabic, Bengali, Thai, and Traditional Chinese. Innovatrics DOT utilizes language-specific models and algorithms that are trained to accurately recognize and process unique characters and text structures.