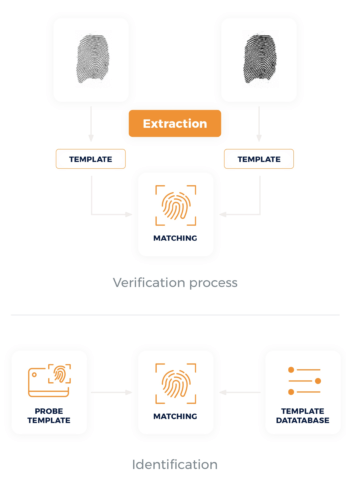
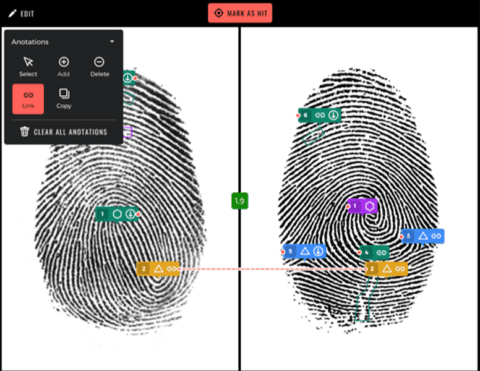
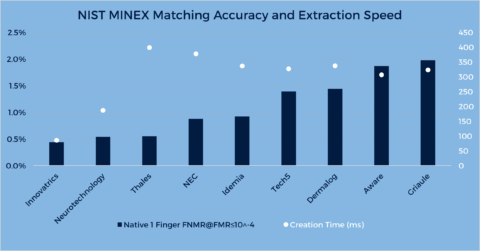
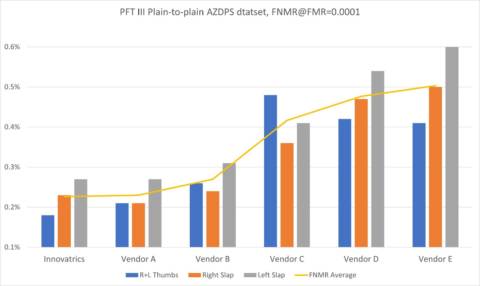
What is fingerprint and fingerprint technology?
Fingerprints are unique patterns of ridges, whorls, and loops found on the fingertips of humans. These patterns, formed during fetal development and unchanged throughout life, serve as distinctive identifiers for individuals. Fingerprint technology utilizes these unique patterns to authenticate and verify identities in various applications. By capturing and analyzing the unique characteristics of an individual’s fingerprint, this technology enables secure access to devices, buildings, and sensitive information. Fingerprint recognition systems employ sophisticated algorithms and sensors to scan and match fingerprints, offering a reliable and convenient method of biometric authentication.
What are the benefits of fingerprint technology?
Fingerprint technology offers a multitude of benefits, making it a preferred choice for biometric authentication. Firstly, its unparalleled accuracy ensures reliable identity verification, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access. Secondly, fingerprint authentication provides convenience for users, eliminating the need to remember complex passwords or carry physical tokens. Additionally, the unique nature of fingerprint patterns enhances security, as each individual possesses distinct biometric characteristics. Furthermore, the speed of fingerprint authentication enables quick access to secured systems or facilities, enhancing operational efficiency. Moreover, fingerprint technology is versatile, with applications ranging from personal devices to corporate security systems, making it adaptable to diverse environments and use cases. Overall, the combination of accuracy, convenience, security, speed, and versatility makes fingerprint technology an invaluable tool for ensuring secure access to digital services and protecting sensitive information.