

Building Trust in Home-Sharing Platforms with Digital Identity Verification Solutions
The advent of home-sharing platforms has revolutionized travel and accommodation. These platforms offer convenience and flexibility by allowing ...
Read more

(This is a part of the series about remote identity verification solutions and how to successfully integrate them into your business. For all parts of the series, click here.)
What you’ll learn in this part:
In the evolving landscape of remote identity verification, ensuring accurate processing of identity documents (IDs) is paramount. As industries adopt remote solutions, the demand for precise, reliable, and secure identity verification continues to grow. This part of the series focuses on the key technologies and challenges in accurately reading and processing identity documents.
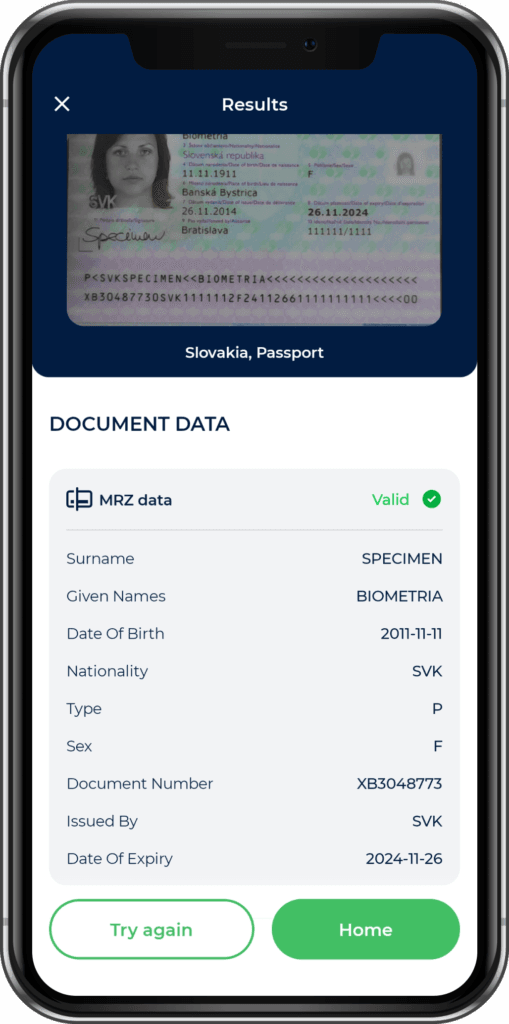
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology has become a cornerstone of identity verification. OCR is essential for quickly and accurately extracting text from ID cards, passports, and other documents. By converting the text from scanned images into machine-readable text, OCR enables systems to capture essential details such as name, birthdate, and document number with minimal user input.
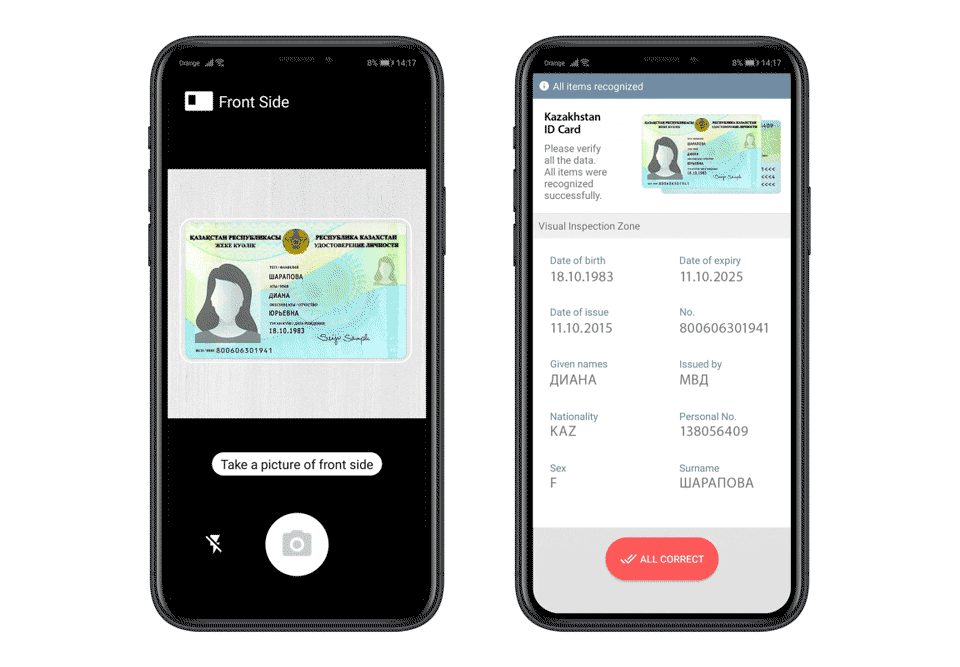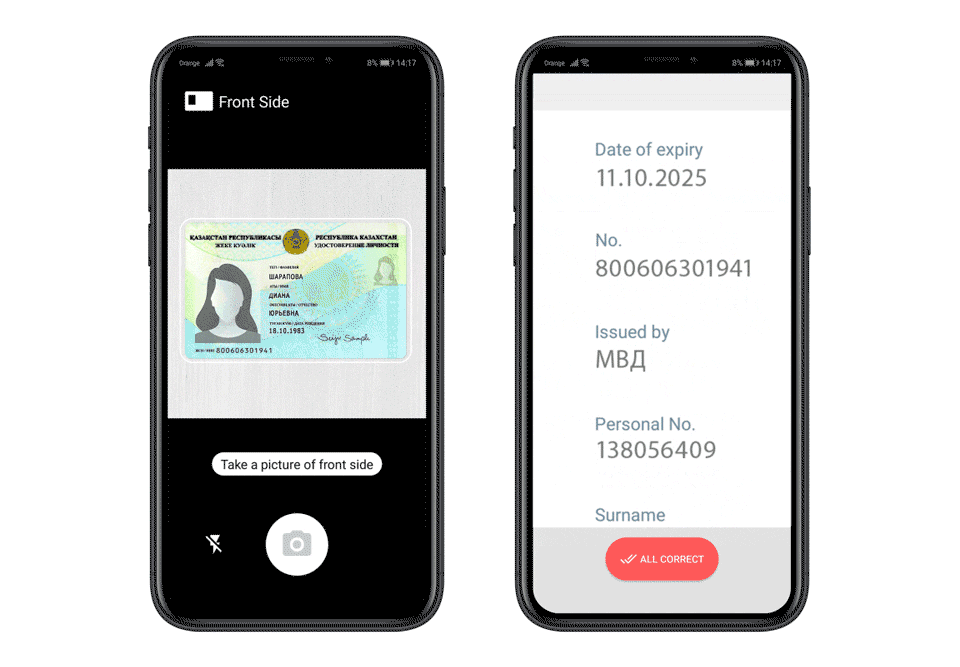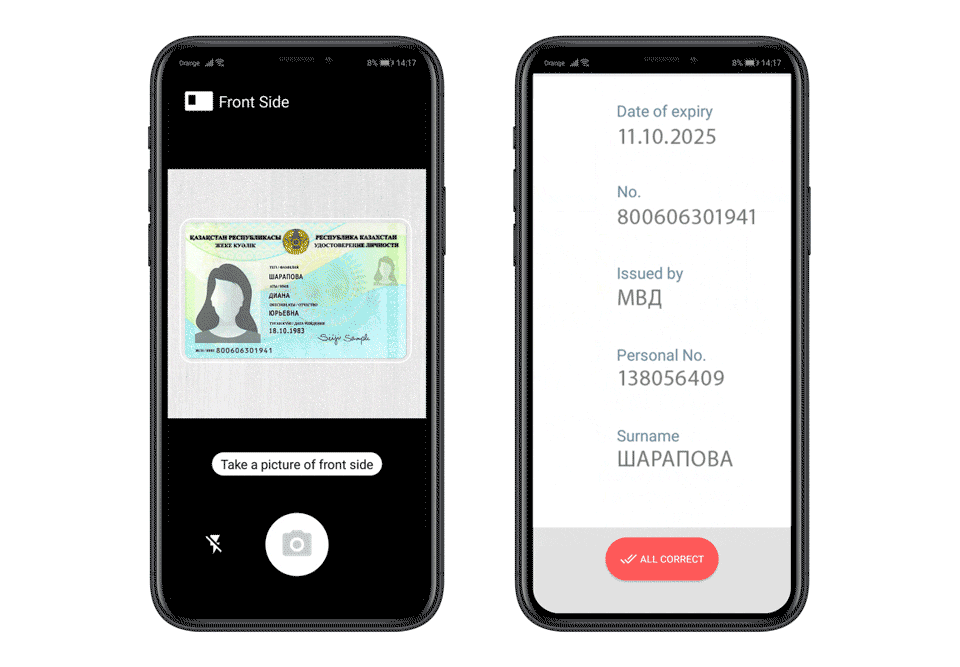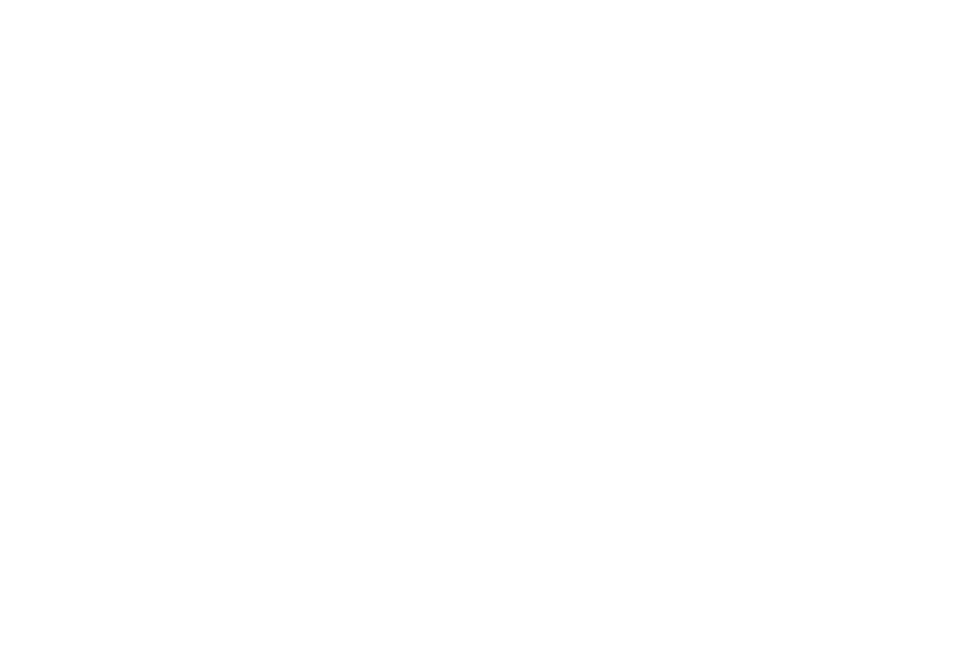

However, OCR’s effectiveness depends on several factors:
Modern OCR systems go beyond mere text recognition. They incorporate AI and machine learning algorithms to improve accuracy, even in less-than-ideal conditions. Some OCR solutions now offer multilingual support, enabling them to process documents from different countries seamlessly.
To ensure that OCR systems work optimally, automatic document detection and capture play a critical role. These systems assist users in aligning their documents correctly in front of a camera, ensuring that the entire document is captured with clarity. Automated capture solutions guide users with visual cues, making the process user-friendly and efficient.
In a typical remote identity verification process, the document detection technology helps in:
This automation minimizes the chances of human error, making the document capture process seamless and reducing the time required for verification.
Although uploading existing photos may seem like a convenient option, it introduces several risks in remote identity verification. One of the primary concerns is the authenticity of the uploaded photo. Pre-existing images can be easily tampered with, making it difficult to ascertain whether the person in the photo is the actual owner of the ID.
With tools like Photoshop readily available, altering an image to commit fraud is relatively easy. This can lead to identity theft and other forms of fraudulent activity. Existing photos may not also meet the standards required for identity verification. Poor lighting, low resolution, and improper angles can prevent accurate facial recognition or OCR processing.
Older photos may no longer reflect the current appearance of the individual. This may result in mismatches during the verification process. Moreover, pre-uploaded photos do not allow for liveness detection, which is crucial for ensuring that the person being verified is physically present and not attempting fraud through static images.
For these reasons, real-time capture of photos during the verification process is preferred. This ensures that the captured image is consistent with the ID being verified and reduces the likelihood of fraud.
Another critical aspect of remote identity verification is detecting anomalies on ID cards. Anomalies can include tampered data, inconsistent fonts, or even counterfeit IDs. Sophisticated verification systems employ advanced techniques to detect these irregularities.
AI-driven systems can compare ID card patterns against known templates, identifying discrepancies in design or format. Many modern ID cards include security features like microprinting and holograms that are difficult to replicate. Verification systems can detect these elements and flag any missing or altered features.
ID cards often include barcodes or QR codes that contain encrypted data. Anomaly detection systems can scan and validate these codes to ensure they haven’t been tampered with. Modern verification systems are now capable of analyzing an ID’s surface for signs of tampering, such as scratches, glue residue, or inconsistent textures. These may indicate attempts to alter the document.
Detecting anomalies is crucial for preventing fraudulent activities, especially in high-security sectors like banking and government services. By catching these irregularities early, businesses can mitigate risks and protect their customers from identity theft.
Near Field Communication (NFC) technology is increasingly being integrated into remote identity verification solutions, especially with the rise of electronic IDs (eIDs). NFC allows for secure data transfer between an NFC-enabled smartphone and an electronic ID card, enabling a more secure and efficient verification process.

NFC can read data directly from an electronic ID card by simply tapping the card against a smartphone. This eliminates the need for manual data entry and reduces the chances of errors. NFC technology uses encryption, making it more secure than traditional methods of reading ID information. The data transfer is almost instantaneous, reducing the risk of interception. Furthermore, NFC-enabled devices can perform real-time biometric matching by reading the data stored on the eID. It compares it with the user’s live biometrics, guaranteeing an accurate identity match.
As more countries adopt electronic IDs, NFC technology facilitates international travel, cross-border identity verification, and access to global services, making remote identity verification more seamless and efficient.
Electronic IDs are becoming more common, with countries like Estonia and Germany leading the way in adopting digital identification solutions. These eIDs can store a wealth of information, including biometric data, which can be verified using NFC technology. This provides a higher level of security compared to traditional physical IDs, making them ideal for remote identity verification.
As remote identity verification continues to evolve, the technologies discussed above will play an increasingly critical role in ensuring security, accuracy, and efficiency. By leveraging OCR, automatic document detection, NFC, and anomaly detection, businesses can provide a seamless and secure verification experience for their customers.
Looking for all or some of these technologies ready for easy integration?
You can find other parts of the Elements of Digital Onboarding Series here